Google Ad Manager Guide: Mastering Ad Success in 2026
The digital advertising world in 2026 is more competitive and fast-paced than ever. As publishers and advertisers face new challenges in maximising ad revenue, understanding the right tools becomes essential.
Google Ad Manager stands out as a powerful ally for those looking to scale, target effectively, and achieve data-driven success. Publishers using the platform can capture up to 69% of ad spend, according to Publift, which highlights the real potential for higher earnings.
By mastering Google Ad Manager, you can unlock streamlined workflows, smarter targeting, and stronger revenue streams. Ready to take your ad strategy to the next level? This guide will walk you through every step, from platform basics and setup to advanced optimisation, reporting, compliance, and the latest trends shaping 2026.
Understanding Google Ad Manager: The Essential Platform in 2026
Navigating the world of digital advertising can feel overwhelming, but understanding
Google Ad Manager gives us a strong foundation to grow. As we step into 2026, this platform stands as the backbone for publishers and advertisers seeking smarter, more profitable ad operations. Let’s break down what makes Google Ad Manager so essential, how it evolved, and the standout features shaping our ad strategies this year.

Evolution and History of Google Ad Manager
Google Ad Manager
has a rich history rooted in innovation. It began as DoubleClick, a pioneering ad serving solution acquired by Google in 2007. This acquisition led to a powerful transformation, with the platform merging DoubleClick for Publishers (DFP) and Ad Exchange (AdX) into a single, unified tool in 2018.
A significant milestone was the adoption of first price auctions in 2019, making bidding more transparent for publishers. Unlike Google Ads or AdSense, Google Ad Manager focuses on the needs of publishers. It offers two main tiers: a free version for up to 200 million impressions per month and a paid Google Ad Manager 360 for large enterprises. For example, major news sites often use GAM 360 to manage their vast and complex inventory.
Core Features and Capabilities
At its heart,
Google Ad Manager brings all your ad inventory together in one place—whether on websites, mobile apps, or video platforms. Real-time bidding and an integrated ad exchange make it simple to maximise revenue from multiple sources.
Key features include advanced targeting by device, location, demographics, and interests. Integration with Google Analytics allows for unified, actionable data. The platform also supports customisable ad units and a range of formats, from banner ads to interactive video. This versatility helps publishers and advertisers create engaging experiences while optimising every impression.
How Google Ad Manager Works
Google Ad Manager acts as both an ad server and an exchange, seamlessly connecting supply and demand. Ad tags are placed on publisher sites, triggering the auction and serving logic every time a page loads. The platform then selects the highest-bidding, most relevant ad in real time.
Managing campaigns means setting up inventory, defining orders, and monitoring delivery. For instance, when a user visits a site, the ad tag communicates with Google Ad Manager, which chooses the best ad based on targeting and bid value. Notably, publishers receive up to 69% of ad spend, with the remaining 31% going to Google, according to Publift.
Google Ad Manager vs. Google Ads: Key Differences
It’s easy to confuse Google Ad Manager with
Google Ads, but their roles are distinct. Google Ads is designed for advertisers looking to run pay-per-click campaigns and target users directly. In contrast, google ad manager is tailored for publishers aiming to monetise their inventory and manage demand from multiple sources.
Retailers might use Google Ads to promote products, while publishers use google ad manager to handle direct deals, programmatic sales, and third-party network competition. For example, a media site can blend direct advertiser deals with programmatic auctions, ensuring every ad slot is filled at the best possible rate.
2026 Platform Updates and Industry Context
In 2026, Google Ad Manager continues to evolve in response to industry shifts. Recent antitrust rulings have prompted greater transparency and fairer competition in ad tech. The platform now features robust compliance tools, privacy updates, and support for first-party data strategies.
AI-powered optimisation and reporting are now central, helping publishers automate decisions and boost revenue. Trends like cookieless advertising, enhanced transparency, and cross-channel reporting are shaping how we achieve ad success together.
Setting Up for Success: Google Ad Manager Account and Inventory
Getting started with Google Ad Manager the right way is crucial for long-term ad success. Let us walk through the essential steps to set up your account, organise your inventory, and build a strong foundation for growth.

Creating and Configuring Your Account
The first step with Google Ad Manager is setting up your account. Visit the platform’s homepage, start the creation process, and connect your preferred email.
Use clear naming conventions for your network and properties, so everything stays organised as your business grows. For those managing multiple sites or clients, a logical account structure is vital. Assign roles—like admin, trafficker, or analyst—to ensure everyone has the right access. Agencies often manage several clients, so proper permissions help avoid confusion and keep data secure.
For a step-by-step walkthrough, the Google Ad Account Setup Guide offers detailed instructions and best practices.
Defining and Organising Inventory
Organising your inventory in Google Ad Manager sets the stage for scalable success. Identify key inventory types: ad units (individual placements), placements (grouped units), and key-value pairs (for custom targeting).
Structure your inventory by site section, device type, or ad format. For example, you might separate desktop banners from mobile interstitials. Use consistent and descriptive names—this will save time as your operations expand.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate:
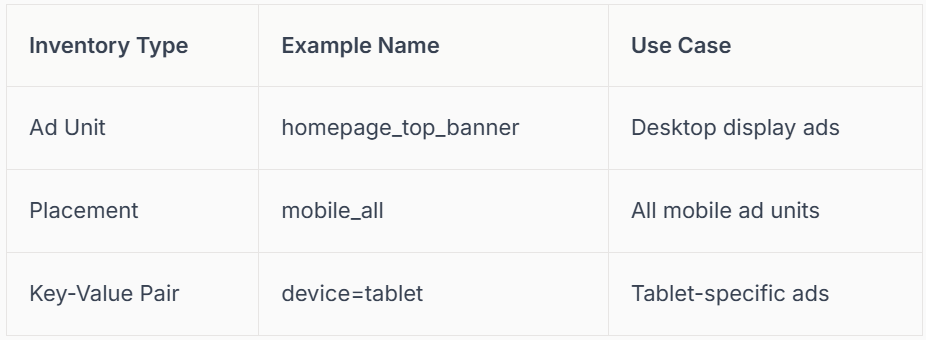
Segmenting your inventory allows for precise targeting and easier reporting.
Setting Up Ad Tags and Integrations
After defining your inventory, generate ad tags in google ad manager for each ad unit. Place these tags directly into your website or app code. This tells the platform where ads should appear.
Integrate with Google Analytics to unlock deeper insights. By linking the two, you can track user actions and build remarketing audiences. For example, you can target users who visited a specific page or engaged with certain content.
Use Analytics audiences to refine your campaigns and drive more value from every impression. This integration bridges the gap between user behaviour and ad performance.
Access Controls and User Management
Managing access in Google Ad Manager keeps your operations secure and efficient. Assign user roles based on responsibilities—admins manage settings, traffickers handle campaigns, and analysts review data.
Adopt security best practices, like two-factor authentication and regular access reviews. Set up audit logs to monitor changes and catch any unusual activity. If you work with external partners or agencies, grant them only the permissions they need.
Scheduled reporting can be set up for different stakeholders, ensuring everyone gets the right information at the right time. Collaboration is smoother when everyone knows their role and has the right tools.
Campaign Management: Trafficking, Targeting, and Delivery
Navigating campaign management in Google Ad Manager is like orchestrating a well-tuned symphony. Each step, from setup to optimisation, plays a vital role in your ad success. Let’s walk through the key stages together so you feel confident, whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro. For even deeper insights, you might want to explore
Campaign Management Strategies 2026.

Step 1: Creating Campaigns and Line Items
Starting a campaign in google ad manager begins with defining your main objective. Are you aiming for brand awareness, lead generation, or direct sales? Once your goal is clear, set up orders, line items, and upload creatives that match your strategy.
Use the platform’s scheduling tools to time your ads perfectly, pacing delivery to fit your marketing calendar.
For example, a campaign might combine display, video, and native formats to reach audiences across several touchpoints.
- Define campaign goals up front
- Create orders and line items for each objective
- Schedule start and end dates, set delivery pace
With these steps, you’re well on your way to a successful launch in Google Ad Manager.
Step 2: Advanced Targeting Strategies
The real power of google ad manager shines in its advanced targeting capabilities. You can reach users by device type, location, language, or custom user segments. Key-value targeting lets you drill down even further, tailoring messages to precise audience traits.
Frequency capping helps avoid ad fatigue, while audience exclusions keep your spend focused on new prospects.
For instance, you might run a campaign targeting only UK mobile users, ensuring maximum relevance.
- Device, geo, and language targeting
- Key-value pairs for granular control
- Frequency capping and exclusions
Mastering these features in Google Ad Manager means every impression counts.
Step 3: Programmatic and Direct Deals
In 2026, balancing programmatic and direct deals is essential for maximising fill rates and revenue. Google ad manager lets you set up programmatic guaranteed, preferred deals, and open auctions, all from one dashboard.
You can manage direct sales relationships alongside programmatic demand, blending the stability of negotiated deals with the scale of programmatic.
For example, a publisher might combine direct sales with header bidding partners to boost competition and earnings.
- Programmatic guaranteed and preferred deals
- Open auction management
- Blending direct and programmatic demand
This flexibility in Google Ad Manager supports both security and growth.
Step 4: Creative Management and Optimisation
Google Ad Manager supports a wide range of creative formats, from standard display to rich media and video. You can rotate creatives, run A/B tests, and measure which formats drive the best results.
Set up approval workflows to ensure all creatives meet compliance standards. For example, test video ads against display to see which gets higher engagement, then optimize based on the findings.
- Display, video, native, and rich media formats
- A/B testing and creative rotation
- Approval and compliance workflows
Creative excellence in google ad manager leads to higher engagement and revenue.
Step 5: Delivery, Forecasting, and Troubleshooting
Monitoring campaign delivery is crucial in
Google Ad Manager. Keep an eye on fill rates, and use forecasting tools to predict how much inventory you’ll have for upcoming campaigns.
If you spot underdelivery, check for targeting conflicts or overlapping line items.
For example, if a campaign isn’t serving as expected, review its targeting and pacing settings to find the issue.
- Monitor delivery and fill rates
- Use forecasting for planning
- Troubleshoot common issues quickly
Staying proactive ensures your Google Ad Manager campaigns deliver as promised.
Step 6: Pricing and Revenue Optimisation
Pricing strategy is key to maximising returns in Google Ad Manager. Set floor prices to protect your inventory’s value, and use dynamic pricing to respond to market demand. Understand Google’s revenue share, where publishers typically receive around 69% of ad spend.
Leverage yield management tools and bring in third-party demand sources for healthy competition. For example, adjust floor prices during peak seasons to capture higher bids.
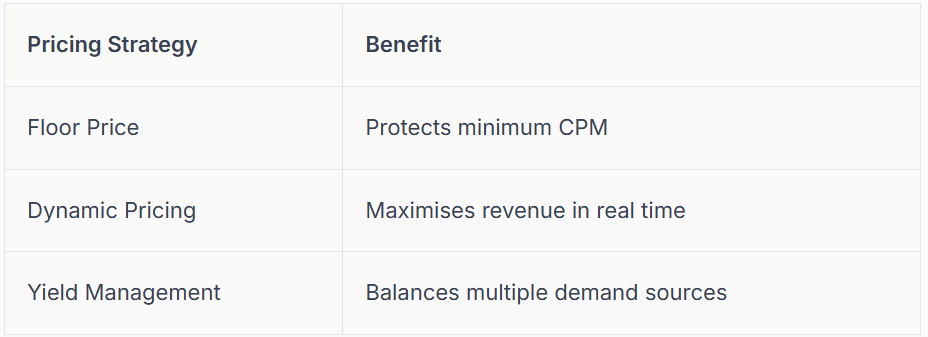
Optimising pricing in Google Ad Manager keeps your ad revenue healthy and growing.
Reporting, Analytics, and Performance Optimisation
Unlocking the full potential of Google Ad Manager in 2026 means mastering the art of reporting, analytics, and performance optimisation. With the right approach, you can turn raw data into actionable insights, helping you maximise revenue and improve campaign effectiveness.

Customising and Scheduling Reports
Google Ad Manager offers powerful custom reporting tools that let you dig deep into your ad performance. You can create tailored reports by choosing specific date ranges, dimensions (like ad unit, device, or country), and metrics that matter most to your business.
Scheduling reports is a smart way to keep everyone in the loop. Set up automated email delivery to share weekly or monthly updates with your team or clients. Export your reports in formats such as CSV or Excel for easy analysis and sharing.
For example, many publishers generate weekly performance reports segmented by ad units. This helps identify trends and opportunities quickly. By making the most of these features, you ensure that your reporting stays consistent, accurate, and actionable.
Analysing Key Metrics for Success
Success with Google Ad Manager relies on understanding and tracking the right metrics. Here are some essentials:

Dive into cohort analysis to spot high-performing segments or placements. When you notice anomalies, such as a sudden drop in fill rate, investigate targeting or inventory changes.
For more practical optimization tips that complement your reporting and analytics, explore these Proven Ways to Improve Google Ads. These strategies often translate well to Google Ad Manager environments.
Leveraging Google Analytics Integration
Integrating Google Ad Manager with Google Analytics gives you a holistic view of both user behaviour and ad performance. This combined data set helps you understand not just what ads are being served, but how users interact with your site before and after engaging with ads.
One powerful tactic is to build remarketing lists in Analytics, then use these for targeted campaigns in google ad manager. By combining bounce rates, session durations, and ad engagement, you can refine your campaigns for better results.
For example, optimize campaigns based on which landing pages have the highest ad engagement. This lets you focus your efforts on areas with the greatest impact. Cross-platform integration means you can react faster and make more informed decisions.
Automated Optimisation and AI Tools
Staying competitive with Google Ad Manager means embracing automation and AI-driven features. The platform now offers built-in recommendations for bids, creative selection, and targeting, helping you boost performance without constant manual tweaks.
Set up rules for automated adjustments, such as pausing underperforming line items or increasing bids for high-value segments. This keeps your campaigns agile and responsive to real-time changes in the market.
For instance, if a particular creative is not meeting your engagement goals, the system can automatically rotate it out for a better-performing option. Automation frees up your time, so you can focus on strategy and growth.
Sharing Insights and Collaboration
Collaboration is at the heart of successful Google Ad Manager operations. Use the platform's sharing features to distribute reports to internal teams, external partners, or clients. Real-time dashboards let everyone monitor results as they happen, fostering transparency and teamwork.
Set up collaborative dashboards that align sales and marketing teams, ensuring everyone is working from the same data. Scheduled reporting and shared insights mean that decisions are always based on the latest performance.
By keeping communication open and data accessible, you create a culture of continuous improvement. This approach helps your entire organisation stay ahead in the dynamic world of digital advertising.
Compliance, Privacy, and Future-Proofing Your Ad Strategy
Navigating the world of digital advertising in 2026 means privacy and regulatory compliance are more important than ever. For any publisher using Google Ad Manager, understanding the rules and adapting quickly is essential for long-term success.
Navigating Privacy and Regulatory Changes
Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA keep evolving, making compliance a moving target. Google Ad Manager offers built-in consent management tools to help you stay compliant, especially when operating in regions like the EEA.
To future-proof your approach, prioritise first-party data strategies and ensure your consent banners are up to date. Using consent mode allows you to tailor ad delivery based on user permissions, which is crucial for maintaining trust and maximising eligible ad impressions.
For example, publishers who adopt consent mode can continue serving personalized ads to users who opt in while respecting privacy choices for others. Staying proactive with these tools helps you build a trustworthy reputation and avoid costly penalties.
Ad Quality, Brand Safety, and Fraud Prevention
Maintaining high ad quality and brand safety is a top concern for anyone using google ad manager. Set up robust blocklists to avoid sensitive or inappropriate categories, and regularly monitor your inventory for invalid traffic and potential ad fraud.
It is wise to partner with trusted verification vendors to help you detect and prevent fraudulent activity. Following Best Practices for Ad Manager API can also enhance your campaign management and protect your inventory from abuse.
Take advantage of built-in tools to review ad creatives before they go live, and use audit logs to track any changes. These steps foster a safer environment for advertisers and users alike.
Staying Ahead: 2026 Trends and Innovations
To stay competitive, embrace the latest innovations in Google Ad Manager. AI-driven targeting and personalisation are transforming how ads reach the right audiences, while new formats like CTV, in-app, and audio ads offer fresh revenue streams.
Transparency and reporting requirements are stricter after recent antitrust changes, so keep up with new features and updates. You can check the Google Ad Manager API release notes to ensure your integrations and workflows remain current.
Early adoption of emerging formats and transparency tools gives you a head start on competitors, helping you capture new demand and maintain advertiser trust.
Maximising Revenue with Multi-Channel Monetisation
Diversifying your monetisation strategy is key to sustainable growth with Google Ad Manager. Integrate with third-party networks and SSPs to tap into more demand sources, and monetise across web, mobile, video, and app environments for maximum reach.
Balance user experience with revenue goals by optimising ad placements and formats. A unified yield management approach lets you compare performance across all channels, making it easier to adjust strategies for the best results.
By staying flexible and proactive, you can adapt to industry shifts and keep your ad revenue strong, whatever the future holds.
Expert Tips and Best Practices for Google Ad Manager in 2026
Striving for excellence with google ad manager in 2026 means embracing both innovation and efficiency. To help you make the most of this powerful ad platform, we have gathered expert strategies that address automation, continual learning, real-world results, and troubleshooting. Let’s dive into the actionable tips that will empower your team and boost your ad performance.
Streamlining Operations and Workflow Automation
Efficiency is at the heart of a successful Google Ad Manager strategy. Automate repetitive tasks such as trafficking, reporting, and optimisation using built-in bulk actions and templates. This frees up your team to focus on strategy and creativity.
- Use bulk creative uploads to save time.
- Automate approvals for faster campaign launches.
- Schedule recurring reports to keep everyone informed.
By implementing workflow automation, you can ensure consistency and accuracy across campaigns. Agencies managing multiple clients with Google Ad Manager especially benefit from these streamlined processes.
Continuous Learning and Platform Updates
Staying ahead in Google Ad Manager requires ongoing education and adaptation. Google regularly introduces new features and updates, so subscribe to official release notes and participate in community forums.
Take advantage of in-depth guides such as Mastering PPC and Google Ads for advanced strategies. For technical teams, regularly review the Deprecation Schedule for Ad Manager API to ensure your integrations remain up to date and compatible.
Attend webinars, join virtual events, and encourage your team to share insights. The more you learn, the more value you unlock from Google Ad Manager.
Case Studies: Real-World Success Stories
Nothing beats seeing Google Ad Manager best practices in action. One publisher increased ad revenue by 20 percent after integrating the platform and optimising across multiple formats.
Lessons from top publishers include:
- Testing multi-channel and multi-format campaigns.
- Adjusting floor prices during seasonal peaks.
- Collaborating closely with sales and marketing teams.
By learning from industry leaders, you can avoid common pitfalls and replicate proven strategies for your own success with Google Ad Manager.
Troubleshooting Common Challenges
Even the best setups encounter issues in Google Ad Manager. Whether you face policy violations, ad disapprovals, or reporting discrepancies, a systematic approach is key.
- Review policy documentation if ads are rejected.
- Cross-check revenue and fill rate data for inconsistencies.
- Investigate drops in fill rate after privacy updates and adjust targeting as needed.
Proactive monitoring and regular audits help you resolve challenges quickly, ensuring smooth delivery and optimal results in Google Ad Manager.
We’ve covered a lot together in this guide, from setting up Google Ad Manager to unlocking new trends for 2026, and I know it can feel like a lot to navigate on your own. The great news is you don’t have to do it solo—especially when it comes to building your local presence and making sure every detail is spot on. If you’d like a helping hand from someone who truly understands both your trade and the ins and outs of Google, we’re here for you. Let’s make your ad strategy and local profile shine—Contact connect SEO Today.












